Linked lists are a way to store a collection of elements. Each element in a linked list is called a node. A node contains two fields: a data field to store the element and a next field to point to the next node in the list. The last node in the list points to NULL.
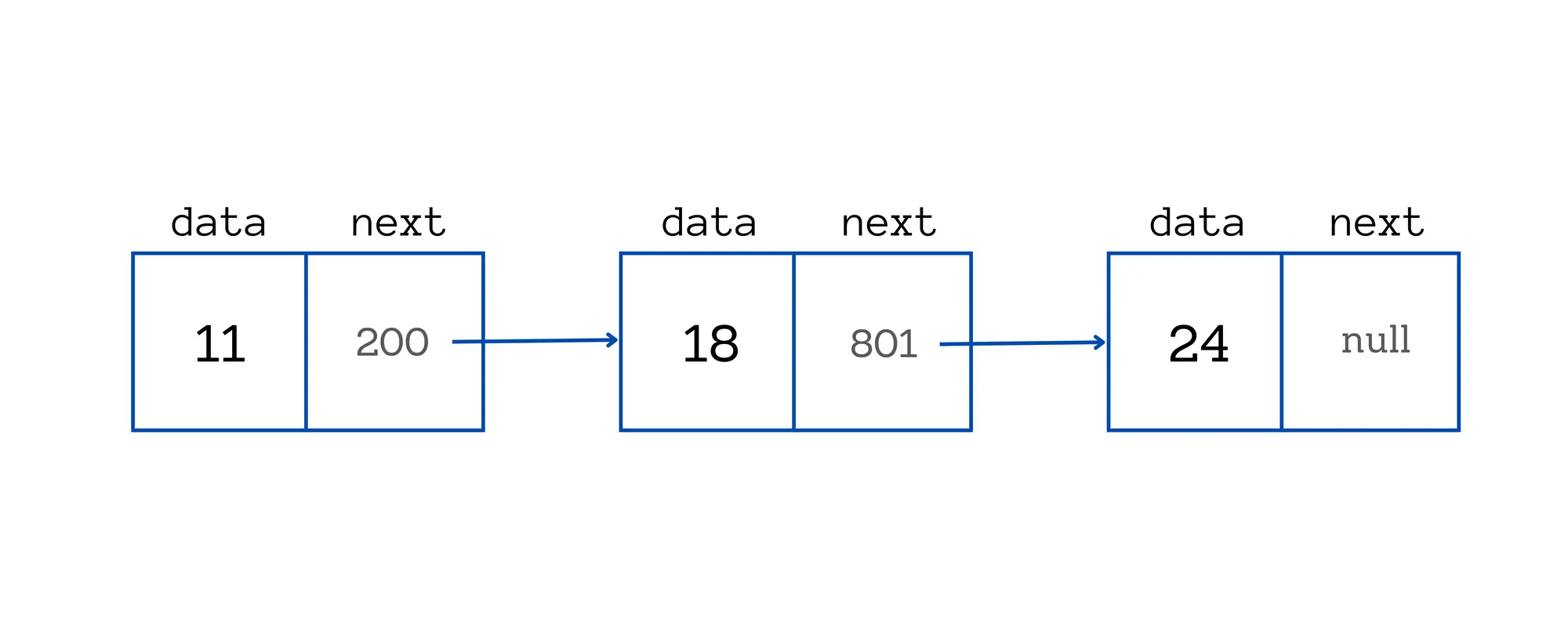
The main advantage of linked lists over arrays is that they can grow and shrink dynamically. The array size is fixed at compile time, while linked lists can change in size at runtime. Also, in comparison to arrays, linked lists do not require contiguous memory locations - each node can be located anywhere in memory.
However, linked lists have slower access times than arrays because elements are not stored in contiguous memory locations.