This study discusses how to sort a linked list using the Bubble Sort algorithm, specifically for sort_list exercise from the 42 curriculum.
Prerequisites
Subject
Write the following functions:
t_list *sort_list(t_list* lst, int (*cmp)(int, int));This function must sort the list given as a parameter, using the function pointer cmp to select the order to apply, and returns a pointer to the first element of the sorted list.
Duplications must remain.
Inputs will always be consistent.
You must use the type t_list described in the file list.h
that is provided to you. You must include that file
(#include "list.h"), but you must not turn it in. We will use our own
to compile your assignment.
Functions passed as cmp will always return a value different from
0 if a and b are in the right order, 0 otherwise.
For example, the following function used as cmp will sort the list
in ascending order:
int ascending(int a, int b)
{
return (a <= b);
}Explanation
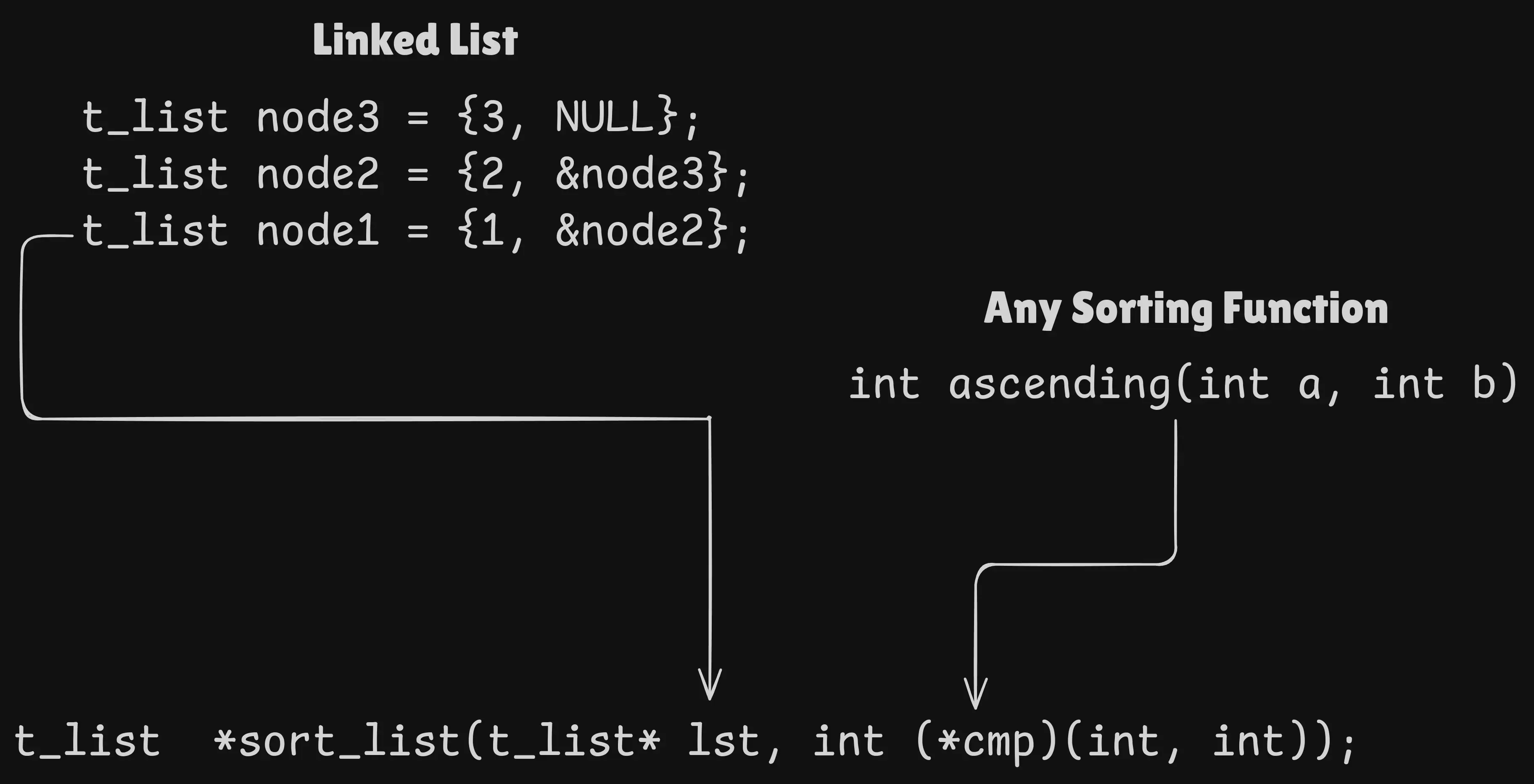
The sort_list function takes a linked list and a comparison function as arguments. The comparison function is used to determine the order in which the elements of the list should be sorted (ascending, descending, etc.).
Solution
#include "list.h"
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
t_list *sort_list(t_list* lst, int (*cmp)(int, int)) {
if(!lst)
return NULL;
t_list *tmp;
int swapped = 0;
while(1){
tmp = lst;
swapped = 0;
while(tmp->next){
if(cmp(tmp->data, tmp->next->data) == 0){
int temp = tmp->next->data;
tmp->next->data = tmp->data;
tmp->data = temp;
swapped = 1;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
if(swapped == 0)
break;
}
return(lst);
}Wait, but how do I test my sort_list function? I got you covered!
int ascending(int a, int b)
{
return (a <= b);
}
int main()
{
// Create a linked list: 1 -> 2 -> 3
t_list node3 = {3, NULL};
t_list node2 = {2, &node3};
t_list node1 = {1, &node2};
// Pass the ref to the first node and the comparison function
t_list* sorted_list = sort_list(&node1, ascending);
// Print the sorted list
t_list* tmp = sorted_list;
while (tmp)
{
printf("%d ", tmp->data);
tmp = tmp->next;
}
return 0;
}