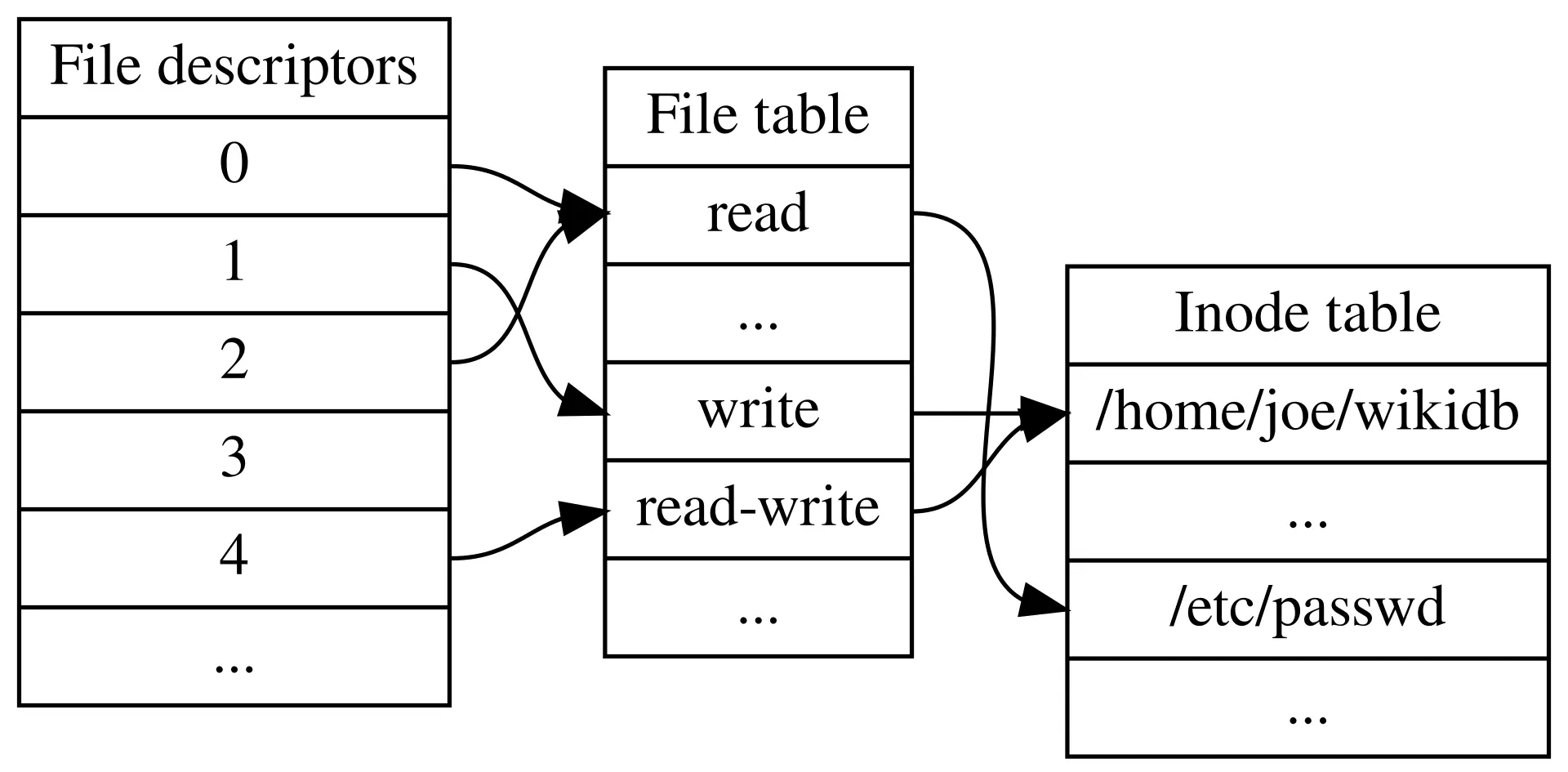
What is an Inode Table?
An inode (index node) table is a data structure in Unix-like file systems that stores key information about each file, except its name and data. Think of it as a database that the filesystem uses to keep track of file metadata and data block locations.
Structure of an Inode
Each inode contains:
- File Metadata:
- File type (regular file, directory, symbolic link, etc.)
- File permissions (e.g.,
rwxr-xr--) - Owner and group IDs
- File size
- Number of links
- Timestamps (access, modification, change)
- Location of the file’s data blocks
- Other Attributes
Key Concepts
- Inode Number: A unique identifier for each file
- Directory Entry: Maps filenames to inode numbers
- Hard Links: Multiple directory entries pointing to same inode
- Soft Links: Special files containing paths to other files
- Block Pointers: Track file data locations on disk
Viewing Inode Information
You can easily check inode number using ls -i and view inode information with stat command:
# List inode number
devnyxie:~$ ls -i filename.txt
9862203 filename.txt
# Display inode information
devnyxie:~$ stat filename.txt
File: filename.txt
Size: 0 Blocks: 0 IO Block: 4096 regular empty file
Device: 259,5 Inode: 9862203 Links: 1
Access: (0664/-rw-rw-r--) Uid: ( 1000/devnyxie) Gid: ( 1000/devnyxie)
Access: 2025-01-19 18:04:10.816862088 +0100
Modify: 2025-01-19 18:04:10.816862088 +0100
Change: 2025-01-19 18:04:42.024653510 +0100
Birth: 2025-01-19 18:04:10.816862088 +0100Inode in Action: How It Works
Interaction with Files
The role of inodes becomes clear when you interact with files by name. Here’s what happens when you run cat simple.txt:
-
Directory Lookup:
The system checks the current directory (or path) to find an entry forsimple.txt. This entry maps the filename to its corresponding inode number (e.g.,9860740). -
Inode Retrieval:
The system retrieves the inode structure from the inode table. This structure contains:- File type, permissions, owner/group, and timestamps.
- Pointers to the data blocks where the file’s content is stored.
-
Data Access:
Using the inode’s block pointers, the system locates the file’s data blocks on the disk and outputs the content to your terminal.
Creating a file
When you create a file:
- The system allocates an inode
- Directory entry links filename to inode number
- File metadata gets stored in the inode
- Data block locations are recorded in the inode